

Sustainable recovery in Southeast Asia faces numerous challenges, yet also presents significant opportunities for green growth. Addressing sustainable issues is crucial for achieving a resilient and sustainable future.
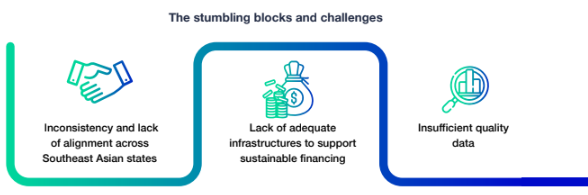
The sustainable issues in SEA primarily lie around environmental, social, and governance (ESG) problems. For environmental problems, the most highlighted issues for environmental problems are environmental degradation, stemming from deforestation, air and water pollution, and the loss of biodiversity. The region's rapid industrialization, urbanization, and agricultural expansion have accelerated these processes, severely impacting ecosystems and human health.
Source: YCP White Paper
Another critical environmental issue is the region's vulnerability to climate change. SEA is highly susceptible to the effects of climate change, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and temperature fluctuations. These changes pose a significant threat to coastal communities, agriculture, and infrastructure, exacerbating poverty and displacement in the region.
Resource overexploitation is also a major challenge in SEA. Activities such as overfishing, unsustainable mining practices, and excessive resource extraction have led to the depletion of natural resources. This overexploitation disrupts ecosystems and threatens the livelihoods of communities dependent on these resources for their survival.
Social inequality further complicates ESG development efforts in SEA. Disparities in access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities create barriers for marginalized communities to participate in and benefit from sustainable initiatives. Addressing these inequalities is crucial for achieving sustainable development goals in the region.
Weak governance and corruption are significant impediments to sustainable recovery in SEA. Inadequate governance structures and widespread corruption hinder the implementation of effective sustainability policies. Transparent and accountable governance is essential for enforcing environmental regulations and promoting sustainable practices that can address the region's pressing issues.
Despite the challenges, SEA has opportunities for its green recovery, particularly through a green growth economy. Green growth in the SEA ensures long-term economic prosperity and environmental sustainability.
SEA possesses immense potential for renewable energy, with solar, wind, and hydropower being particularly promising sources. Countries like Indonesia, the Philippines, and Vietnam actively invest in renewable energy projects to lessen their reliance on fossil fuels and curb greenhouse gas emissions. The expansion of renewable energy infrastructure has environmental benefits, stimulates job creation, lowers energy costs, and enhances energy security.
Implementing sustainable agricultural practices is crucial for SEA's development, in addition to renewable energy. Techniques such as agroforestry, organic farming, and precision agriculture can boost crop yields while minimizing environmental impact. Sustainable agriculture enhances food security, supports rural development, and contributes to mitigating climate change.
Furthermore, developing green infrastructure is essential for reducing environmental footprints in SEA. This includes constructing eco-friendly buildings, improving public transport efficiency, and implementing sustainable urban planning. Green infrastructure investments enhance living standards, reduce pollution, and stimulate economic growth.
Adopting a circular economy model is another vital aspect of SEA's sustainable development. This approach focuses on reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling, thereby promoting sustainable economic growth. By designing products for longevity and recyclability, companies can minimize waste generation and conserve resources, contributing to a more sustainable future for the region. Overall, SEA can accelerate its sustainable recovery by leveraging renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, green infrastructure, and circular economy principles.
Source: https://ycpsolidiance.com/white-paper/accelerating-sustainable-recovery-southeast-asia

Unlocking Opportunities in the SEA Digital Financial Services Landscape
In recent years, Southeast Asia (SEA) has emerged as a hotbed for fintech innovation, transforming the financial landscape across its diverse markets. This transformation is characterized by a surge in digital financial services (DFS), revolutionizing how individuals and businesses manage their finances. However, the journey is not without its challenges, and understanding these is crucial for stakeholders aiming to navigate this rapidly evolving sector.

Leading the Charge: Major Players in SEA’s Digital Lending Market
The fintech lending market in SEA is poised for substantial growth, including digital lending which is set to surpass digital payments as the primary revenue driver for the region's digital financial services sector by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33%. This growth is fueled by the widespread adoption of automated loan origination processes and the seamless integration of financial services into digital platforms.

How SEA Startups are Navigating Funding Challenges
The startup ecosystem in Southeast Asia (SEA) has long been a vibrant hub for innovation and growth. However, recent global economic shifts and the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic have ushered in a new era of funding challenges.

Driving Cross-Border Growth: Regional Logistics Initiatives in Southeast Asia
The logistics landscape in Southeast Asia (SEA) has undergone significant improvements. The SEA logistics market was valued at over USD 497 billion in 2020 and is projected to expand further in the coming years. The SEA logistics market is driven by various regional initiatives and government policies to enhance connectivity, efficiency, and competitiveness across the ASEAN. These initiatives have facilitated smoother cross-border trade and stimulated investment and innovation within the logistics industry.